The Ultimate Guide to Identifying House Plant Pests: With Pictures of Pest and Damaged Plants
The most important part of preventing and treating common houseplant pests is the ability to identify them, understand what they look like, what kind of damage they cause and how they impact the plants. In this article, we will highlight all the different houseplant pests, their characteristics and how best to treat your houseplants. Each pest highlighted will have accompanying pictures of damaged plants that will help you to identify them yourself.
Overview of Common House Plant Pests
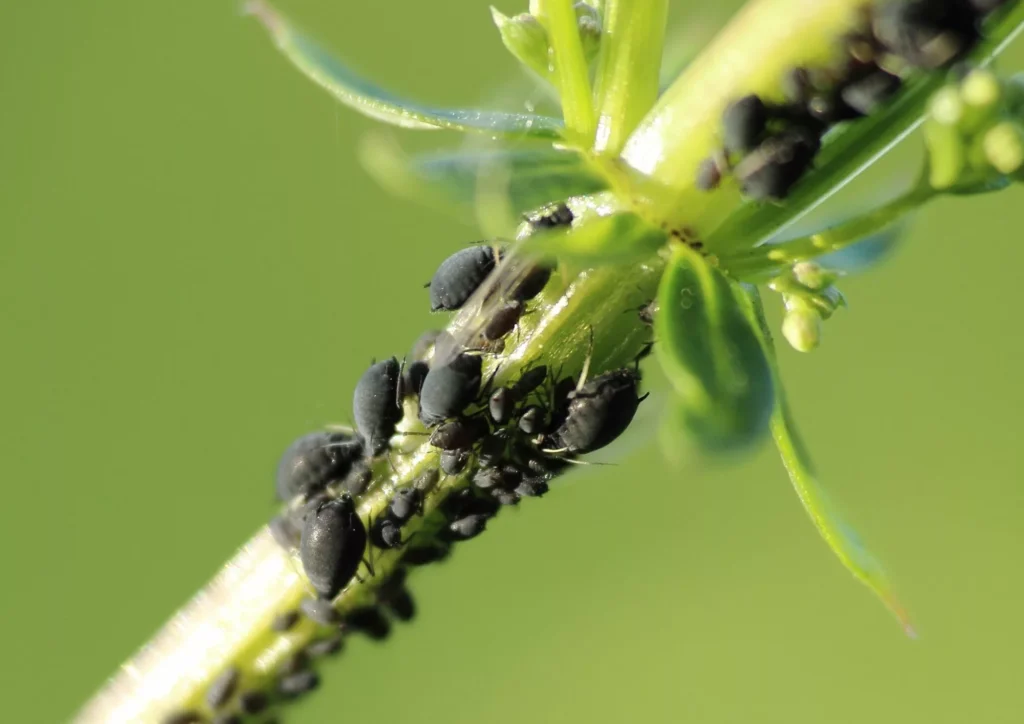
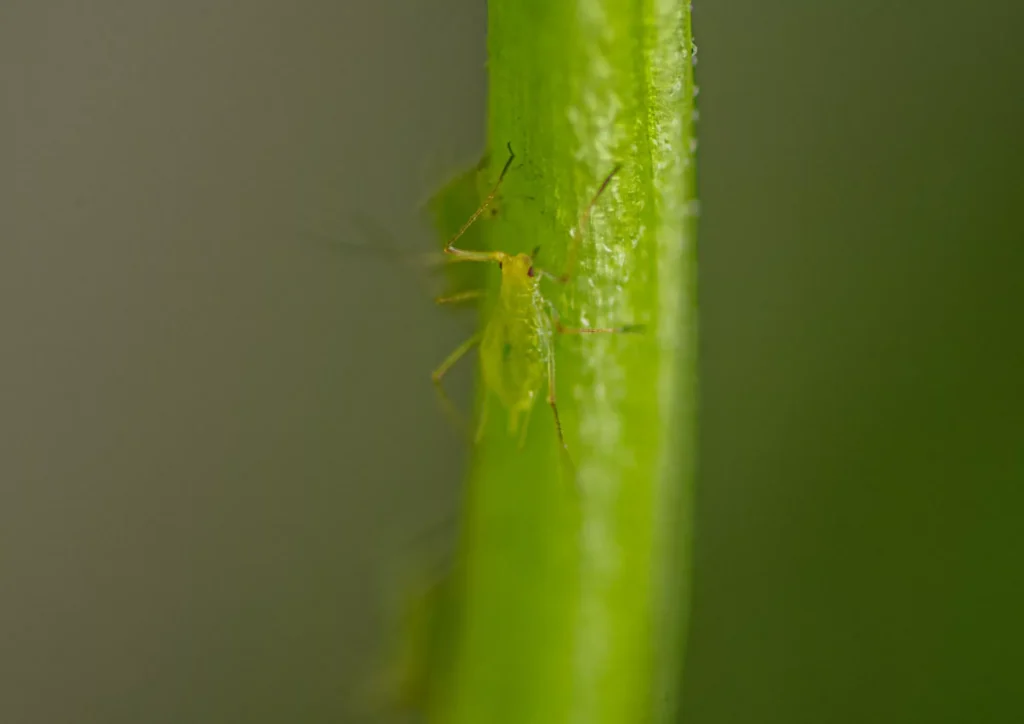
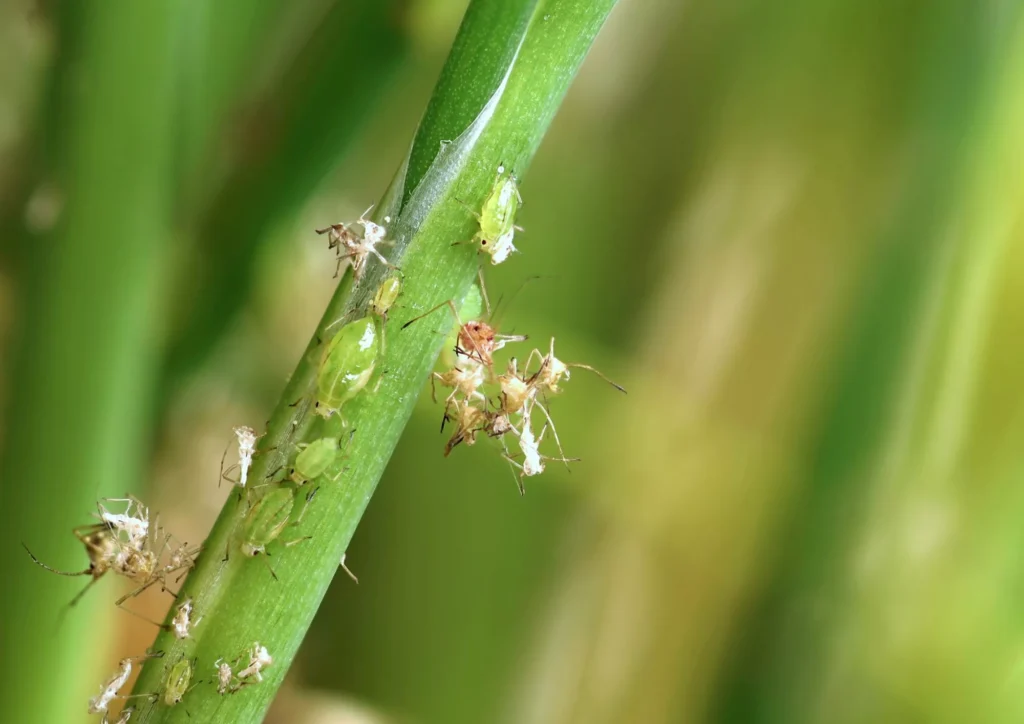
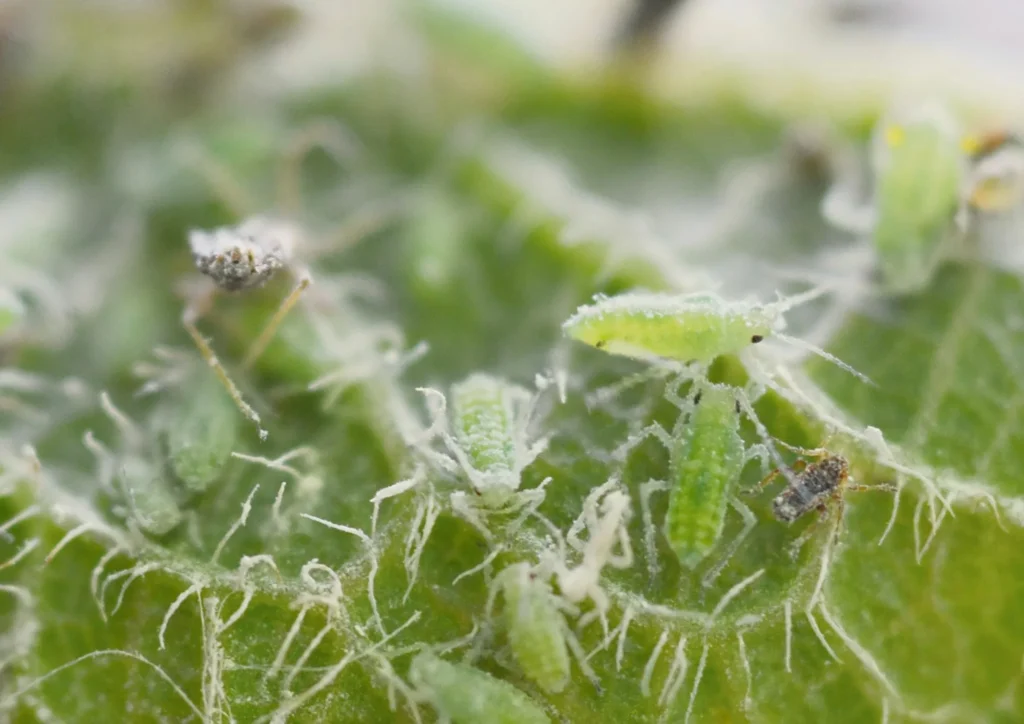
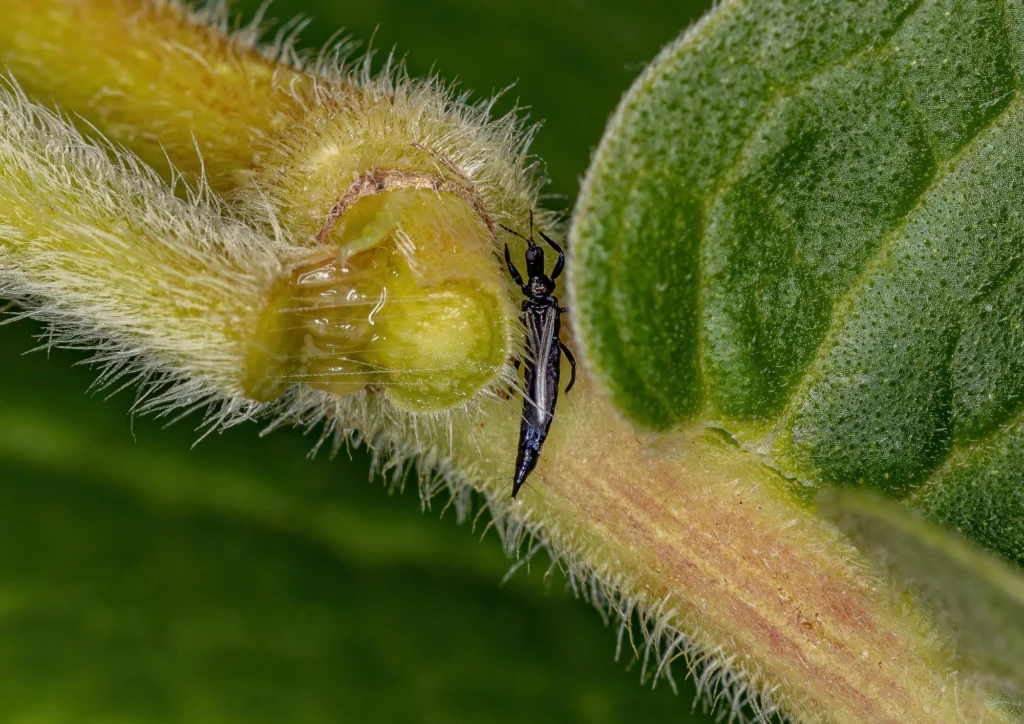
Aphids: The Sap-Sucking Invaders Insects
Characteristics
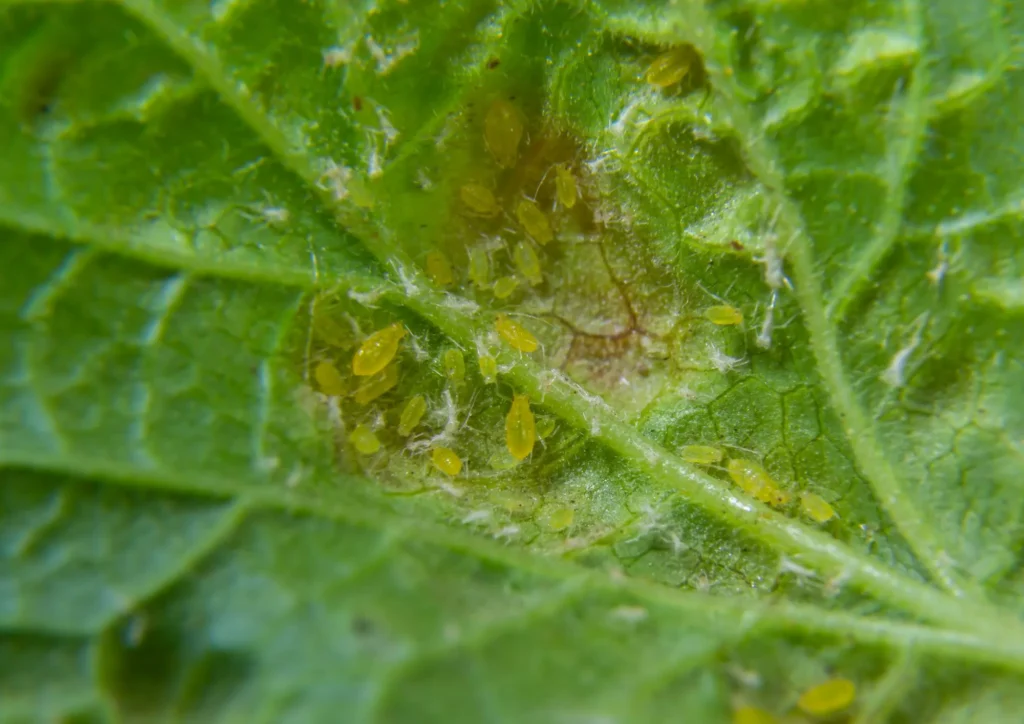
Aphids are minuscule, pear-shaped insects with soft bodies that come in many colours including green, yellow, brown, red, or black. Sometimes they have wings but there are also wingless aphids. Houseplants prone to aphids are Ficus, Dieffenbachia, Philodendron, Monstera, Pilea, Ferns and Carnivorous plants.
Signs of Infestation
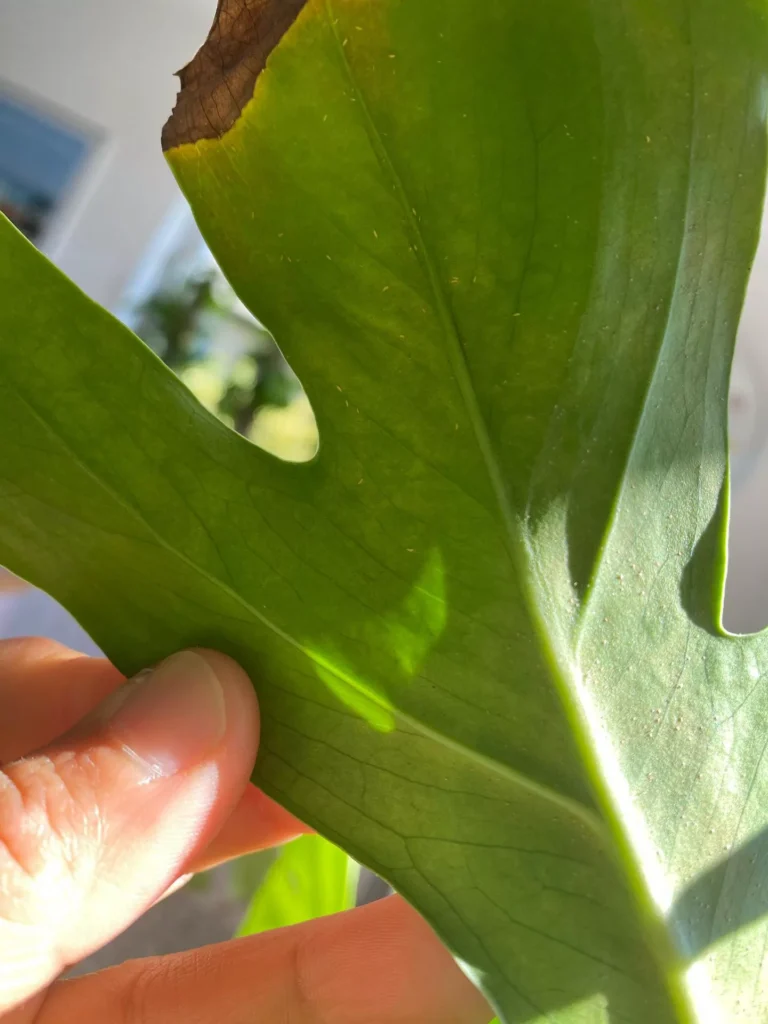
Aphids often leave a trail of sticky substance known as “honeydew” on the leaves and stems of the plant. You may also notice that the new growth appears twisted, curled and deformed. They are usually hidden inside furled leaves or on the undersides of leaves. Aphids do not move fast and typically stay together in clusters.
Impact on Plants
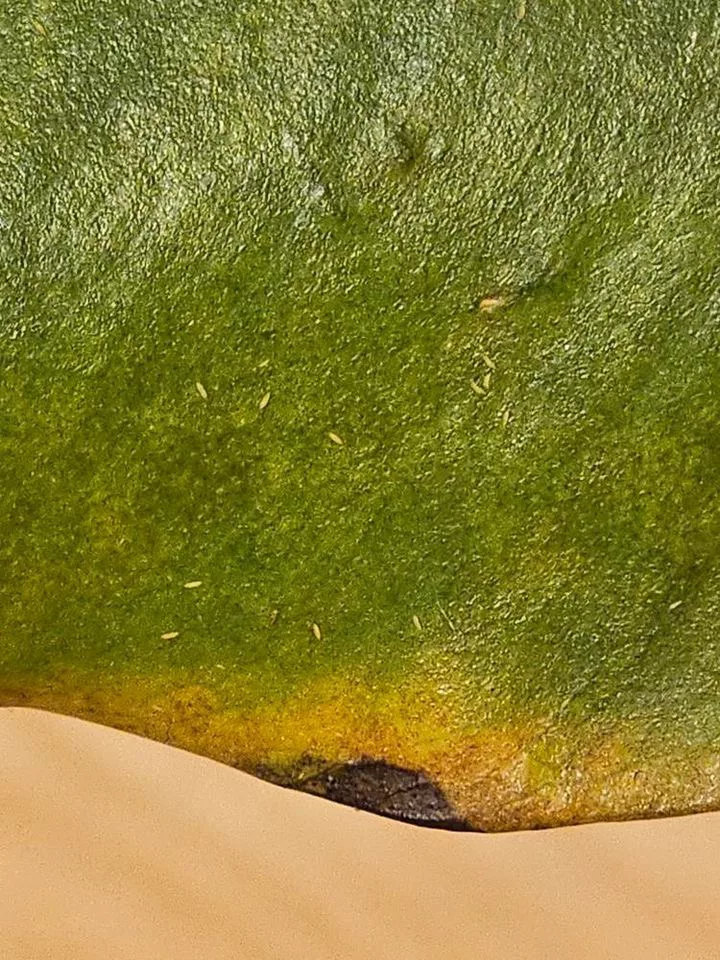
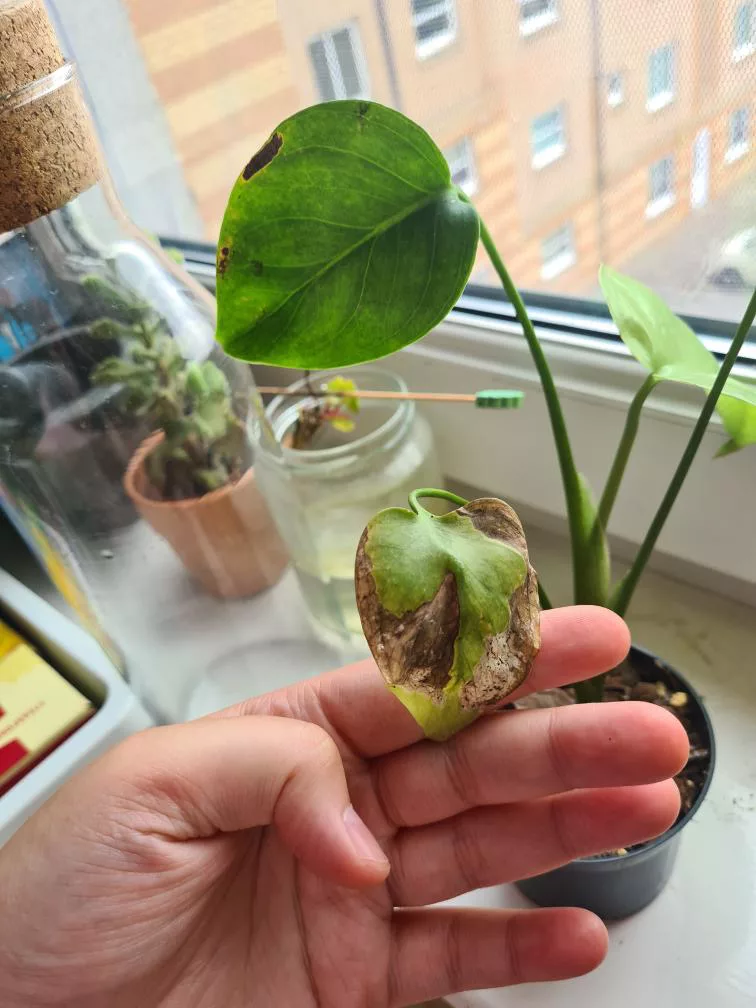
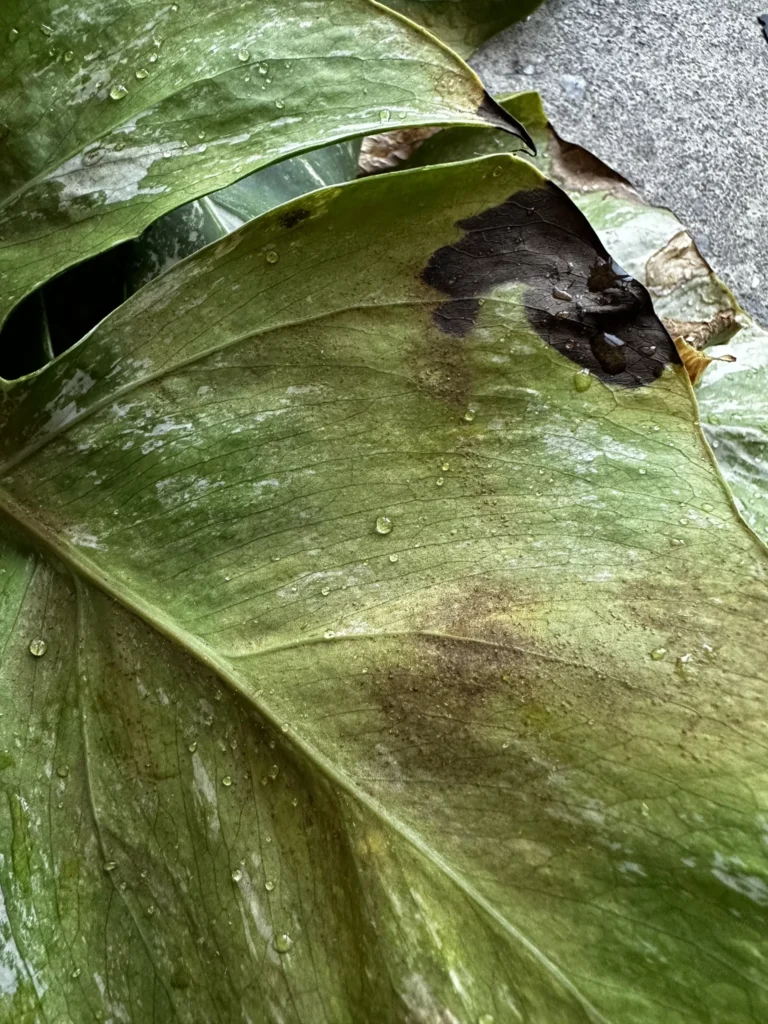
Aphids cause damage by sucking sap from leaves which usually leads to yellowing, deformed leaves and decreased growth rate. The sticky honeydew can attract pollinators but also other pests and increase the chance of sooty mould Ascomycete fungi.
Treatment Strategies
In case of minor infestations, you can try to remove aphids with water, a strong blast from the showerhead can knock them off the plants. In severe cases, consider using systemic biological controls (for example introducing natural predators – ladybugs). Spraying the plant with hydrogen peroxide solution can help with preventing and treating outbreaks. If you want to use pesticides, choose non-toxic and biodegradable options that will not harm pollinators, other animals, and the environment.
Spider Mites: The Web-Spinning Tiny Pests
Characteristics
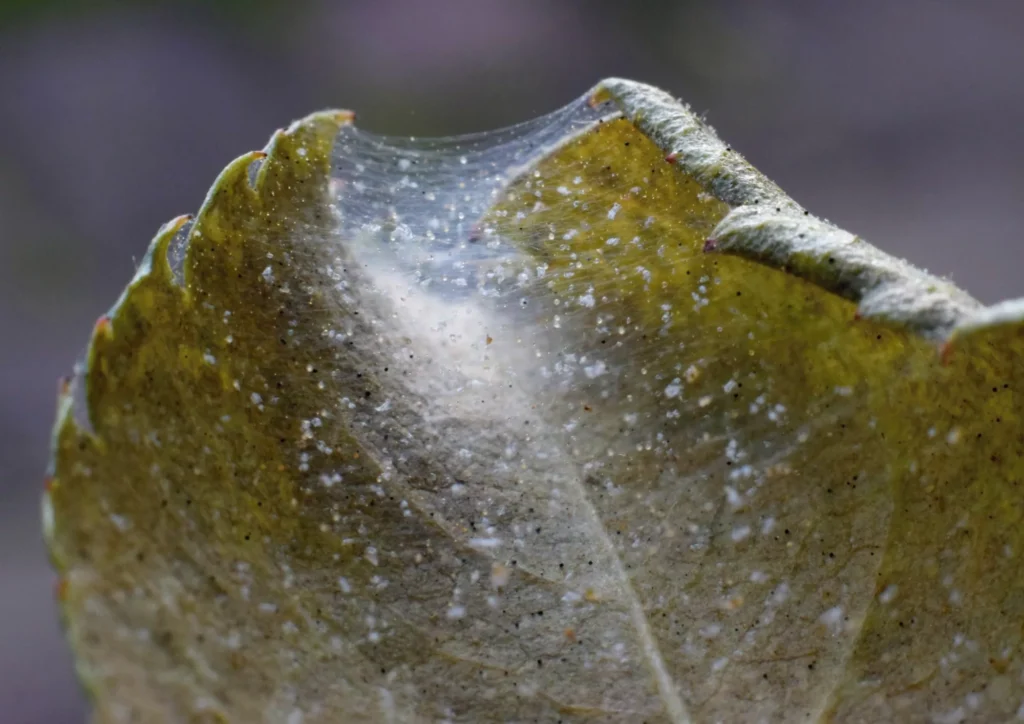
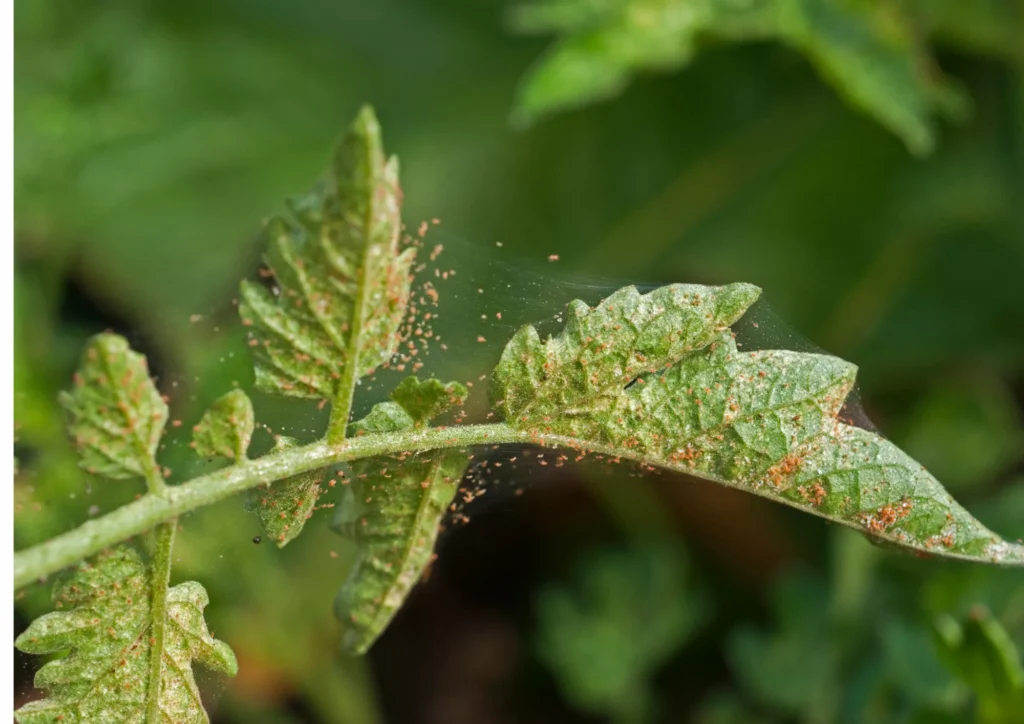
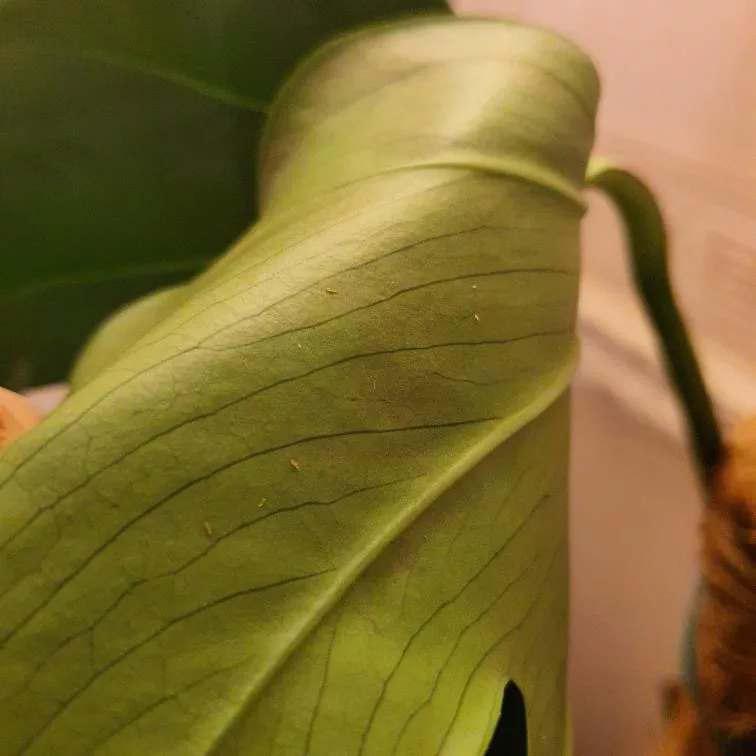
Spider mites are extremely tiny—almost microscopic—pests and are usually red or black. With an average size of 0.5mm or smaller, these arachnids are often hard to detect until they cause substantial damage to plants. Spider mites’ movement is not noticeable, they are usually staying in one location, focusing on sucking sap from the plant. Plants prone to spider mites are Calathea, Maranta, Aspidistra, Alocasia, Chamaedorea, Strelitzia and Hedera.
Signs of Infestation
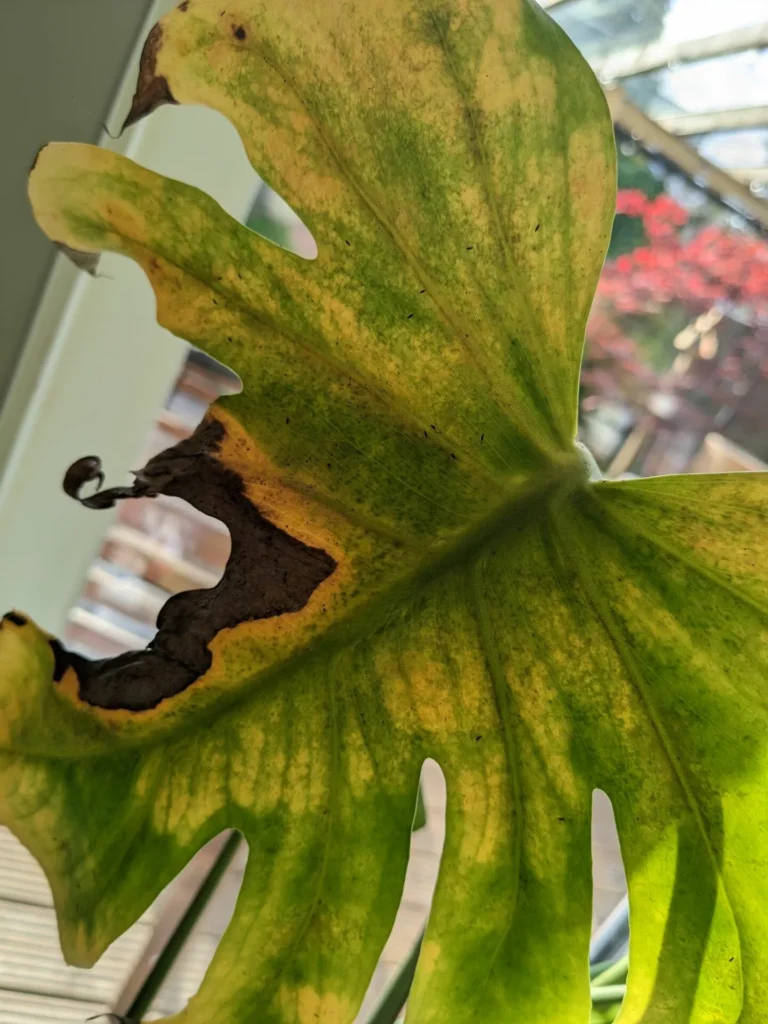
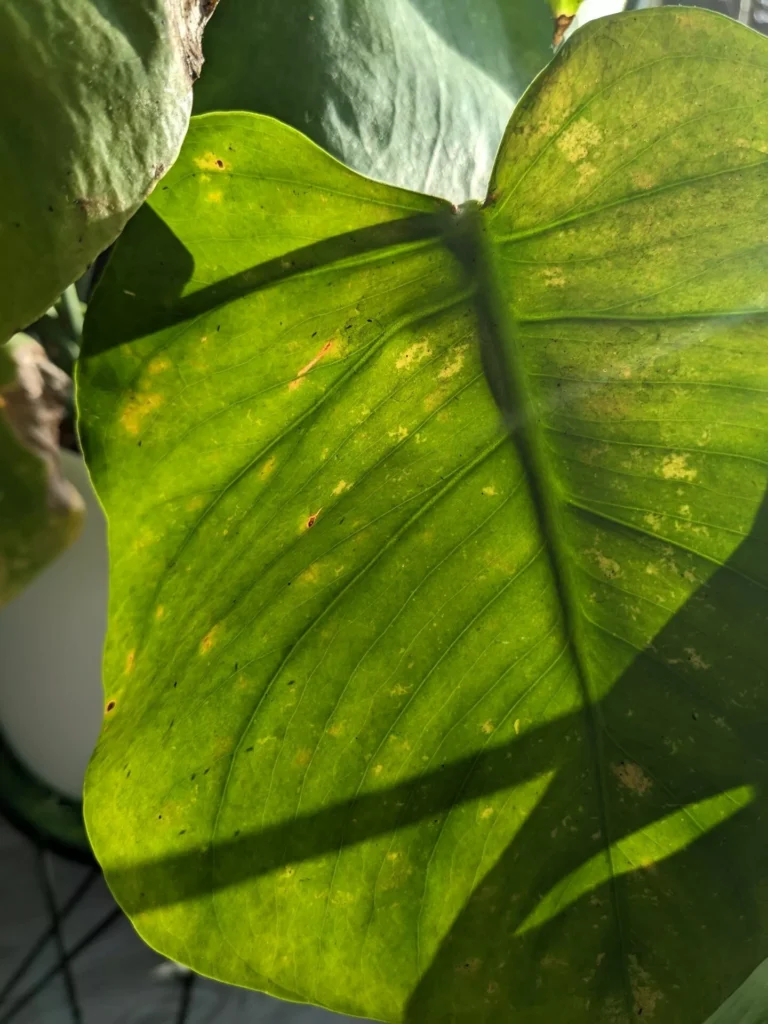
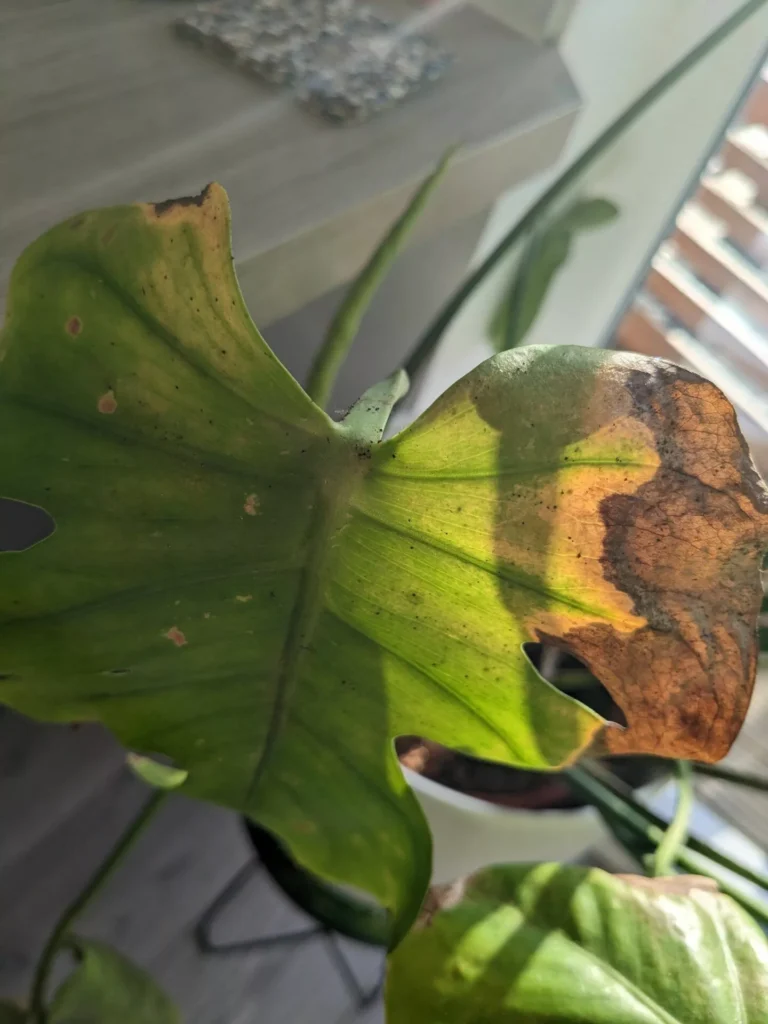
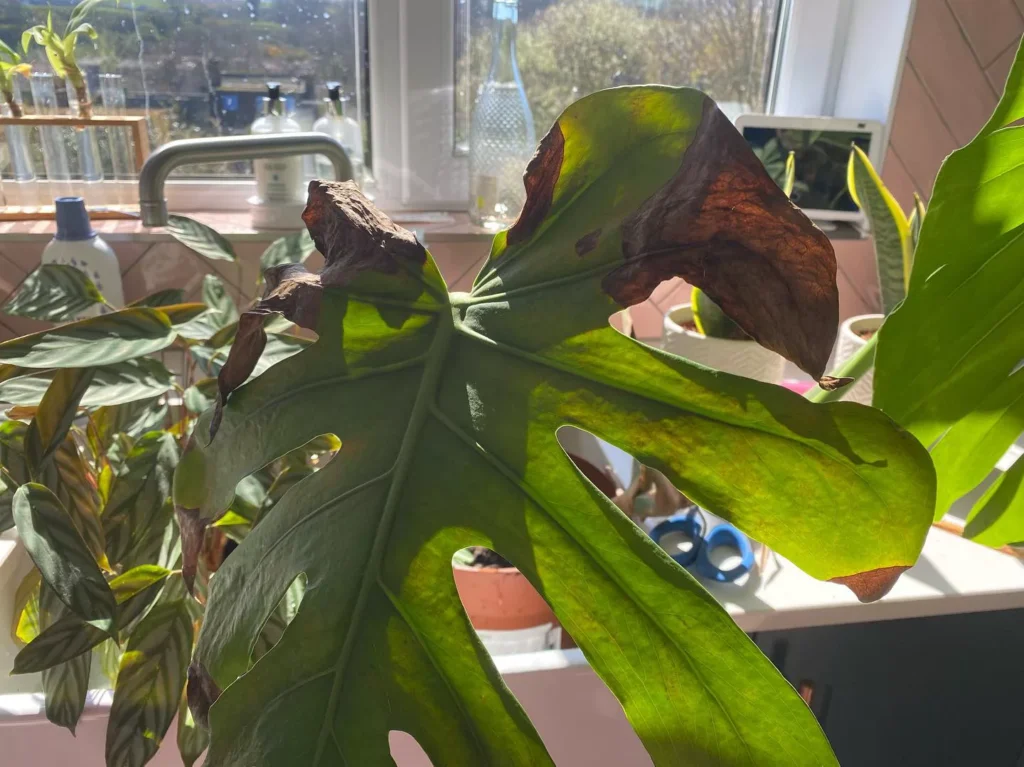
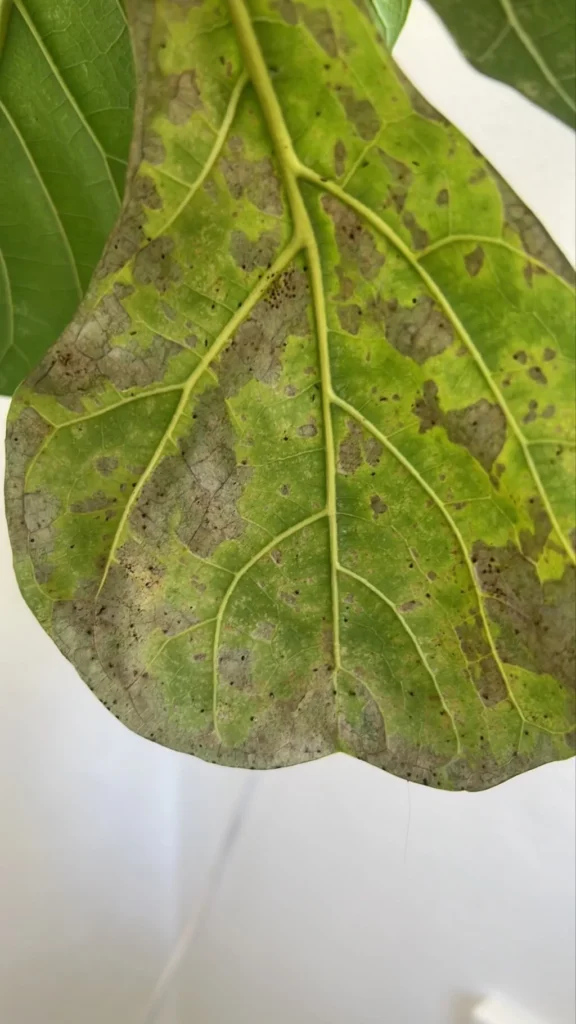
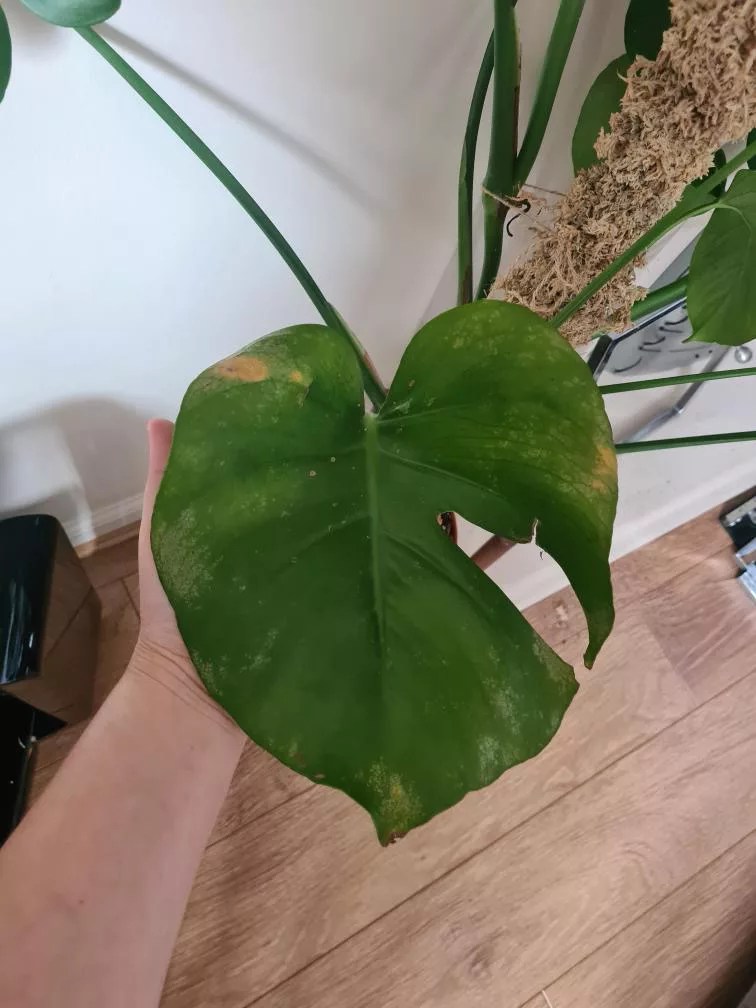
One of the most distinct signs of a spider mite infestation is yellow and brown tiny spots in locations where mites were sucking the sap. With time damage will spread all over leaves and turn them yellow and brown. As a result, leaves will slowly die and the plant will not have the energy to produce new growth. In heavy infestation, spider mites create silky, fine webbing which is similar to spider webs.
Impact on Plants
Spider mites can severely damage the plant, drain all nutrients and often lead to death of the plant.
Treatment Strategies
Spider mites typically prefer dryer and hot environments, increasing humidity and regularly cleaning leaves with water or hydrogen peroxide solution can help prevent outbreaks. It is recommended to use biological spider mite prevention to maintain spider mites population or specialised miticides in case of outbreaks. You can also use non-toxic pesticides to help you fight spider mites in an eco-friendly way. You can try also neem oil and increase humidity as spider mites thrive in a dry environment.
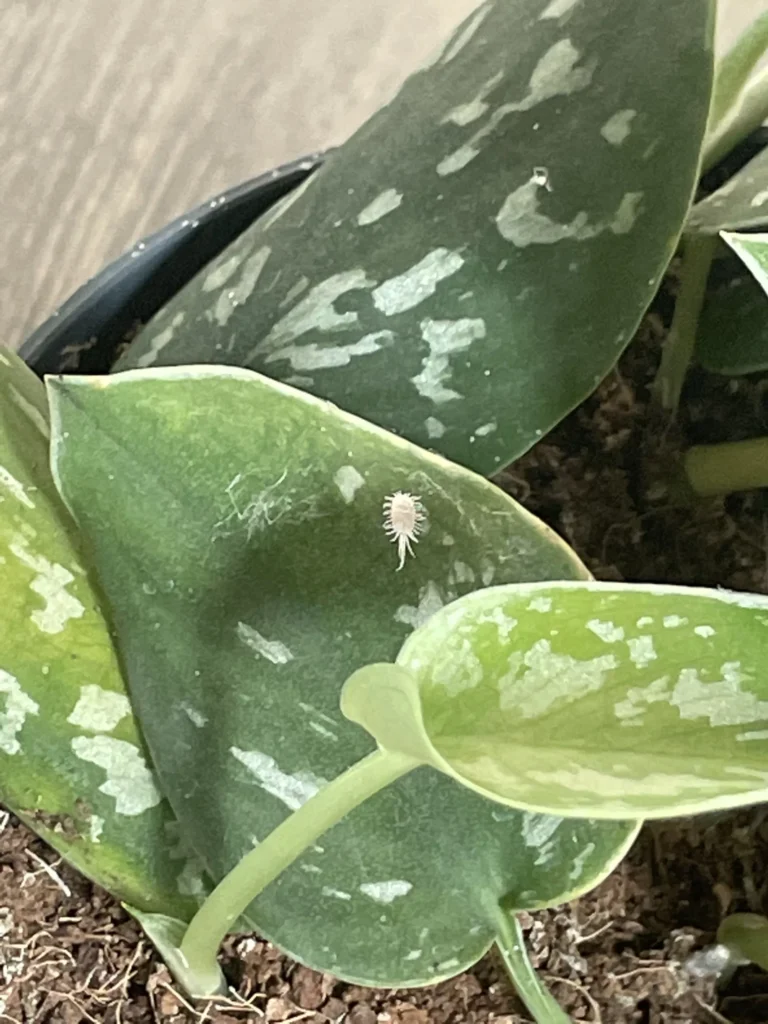
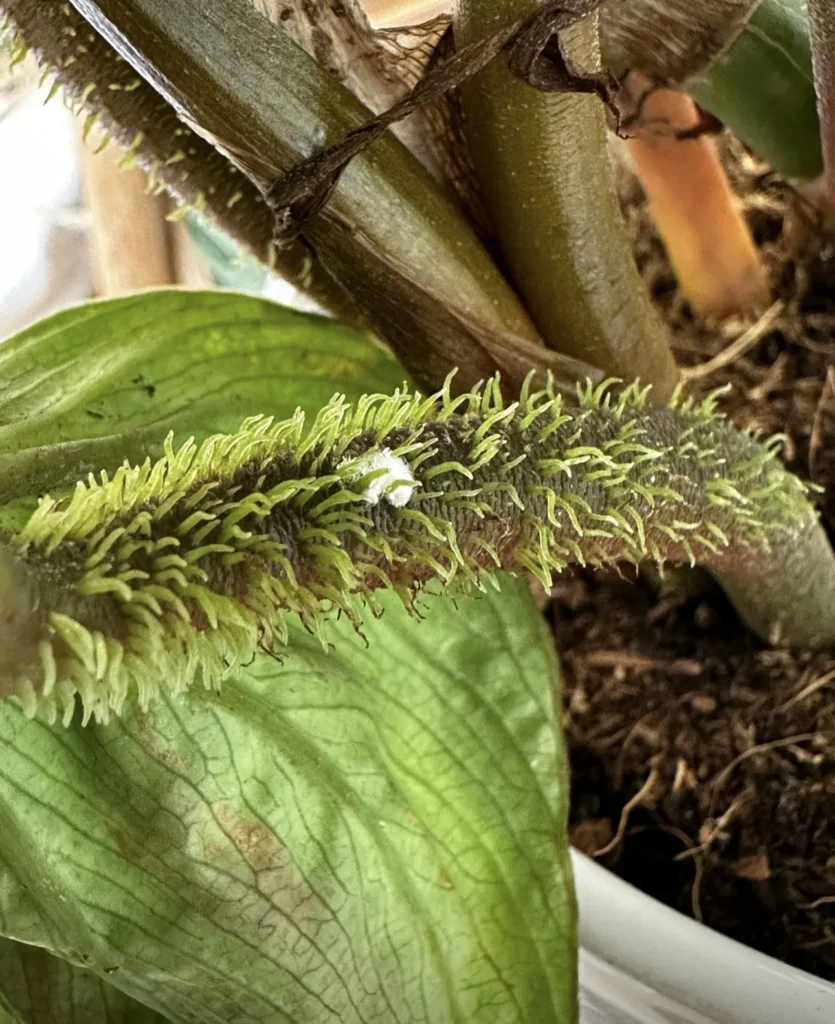
Mealybugs: The Cotton-Like Bugs
Characteristics
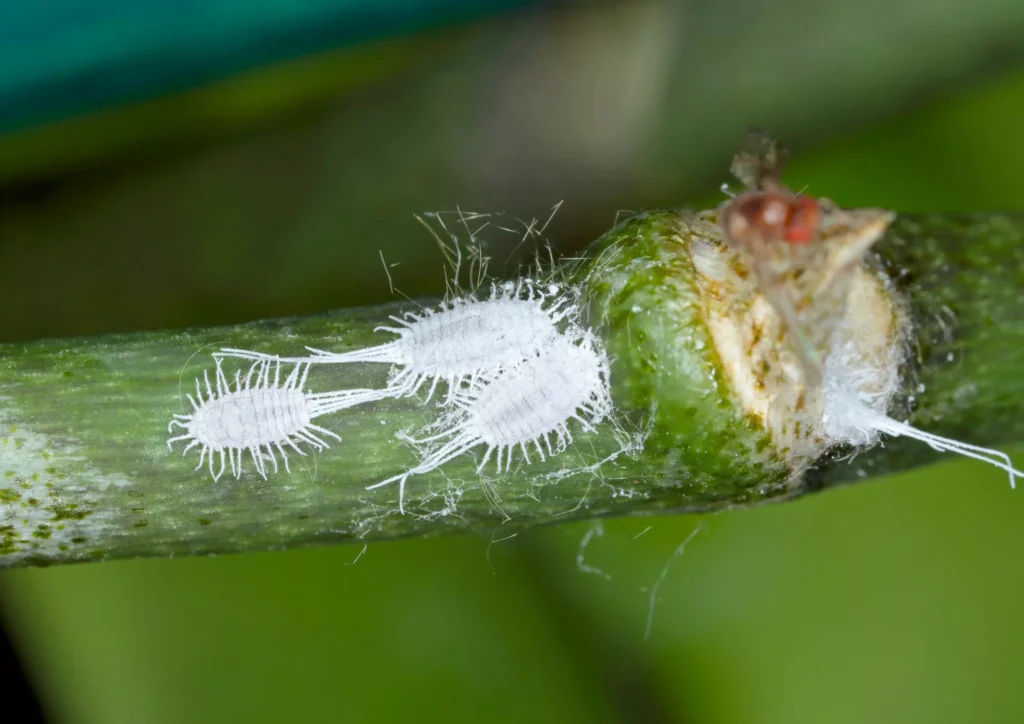
Mealybugs are small, fluffy, and have a white cottony appearance. You can spot them with a magnifying glass, often found hidden in the leaf axils, the undersides of leaves, stems and inside furled leaves. Mealybugs move but rather slowly or stay in the same spot for a longer period. If you are not sure if this is a mealybug or dust you can squeeze it and if you see a pinkish/orange colour then is a mealybug. Houseplants prone to mealybugs are Hoya, Sedum, Peperomia, Pilea, Philodendron, Monstera, Aeschynanthus, Fittonia, Maranta, Calathea and a variety of succulents and cactus plants.
Signs of Infestation
If the growth rate of the plant slows down and you can spot white, fluffy creatures then your plant is infested with mealybugs.
Impact on Plants
Mealybugs feed on the plant’s juices, sucking nutrients from leaves. The sticky honeydew produced by the pest may increase the chance of sooty mould Ascomycete fungi. Mealybugs will significantly weaken plants and decrease growth rates.
Treatment Strategies
Mealybugs can be removed by a cotton bud soaked in rubbing alcohol. Cleaning leaves with hydrogen peroxide solution works well as a treatment and prevention. If you want to use pesticides, choose non-toxic and biodegradable options that will not harm pollinators, other animals, and the environment.
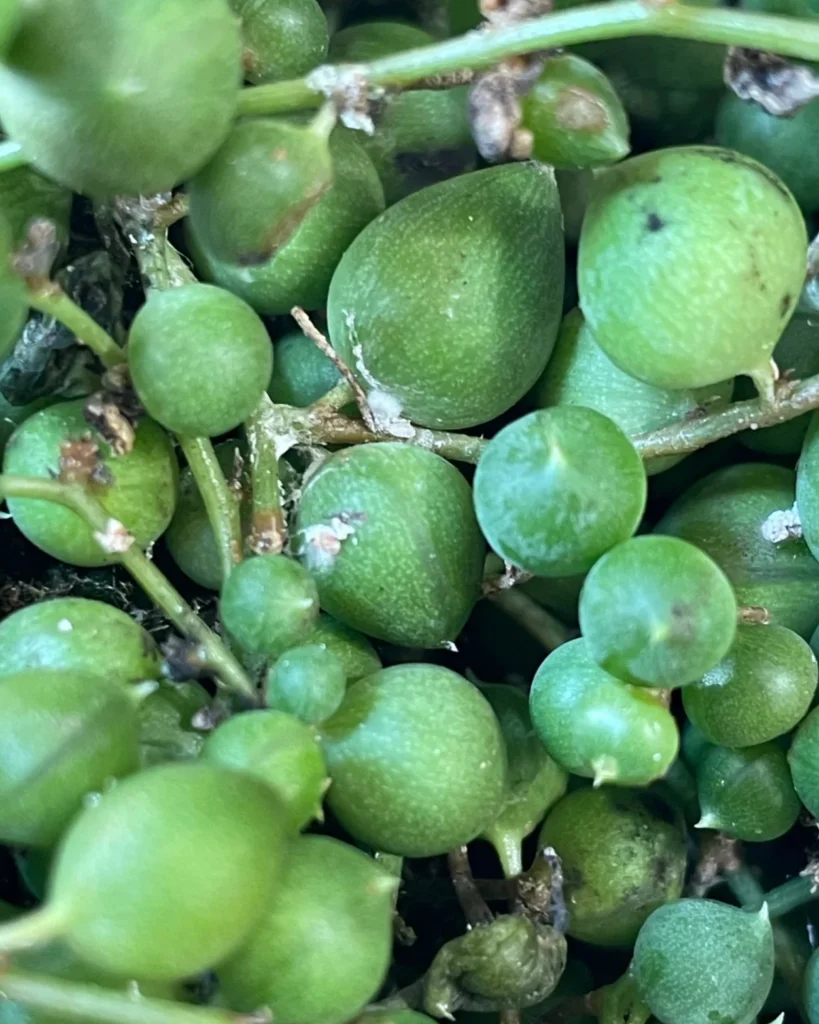
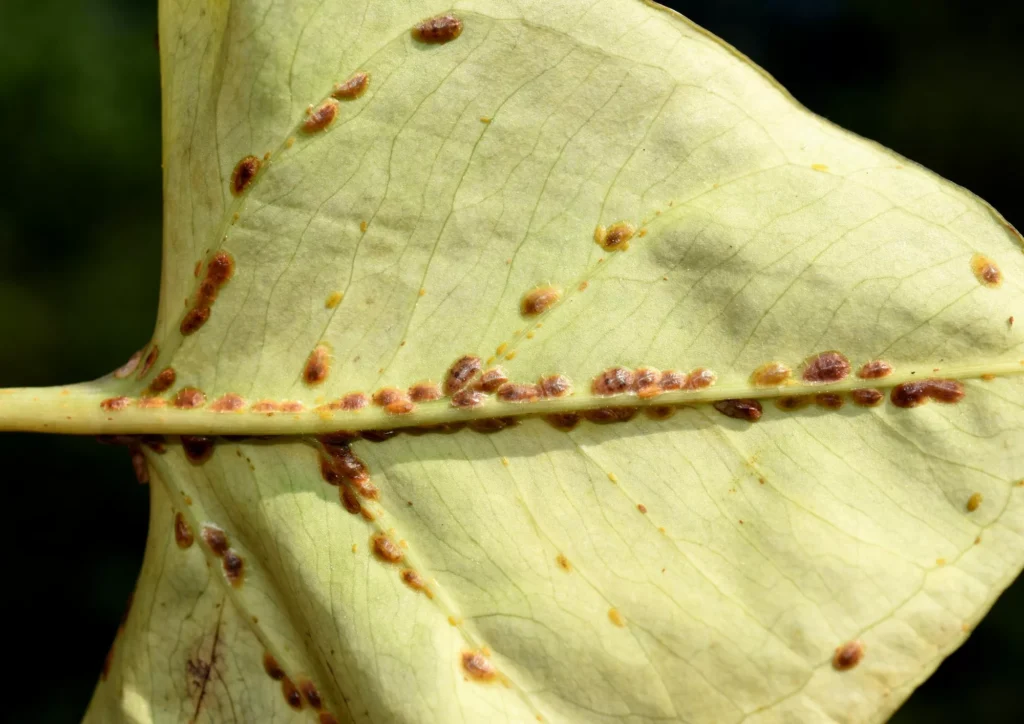
Scale: The Hard-Shelled Sap-Suckers
Characteristics
Scale insects have a hard, shell-like, waxy covering and are generally immobile. They attach themself firmly to stems and leaves.
Signs of Infestation
Look for yellowing leaves and a sticky substance covering leaves and stems. The sticky honeydew can attract pollinators but also other pests and increase the chance of sooty mould Ascomycete fungi.
Impact on Plants
Scale insects suck sap, weakening the plant, causing yellowing leaves and negatively impacting the growth rate.
Treatment Strategies
Scale can be gently scratched from stems and leaves with sharp tools or fingernails. Rubbing alcohol will help to remove them with a cotton bud. If you want to use pesticides, choose non-toxic and biodegradable options that will not harm pollinators, other animals, and the environment.
Thrips: The Tiny Black Insects
Characteristics
Thrips are tiny, elongated insects, varying in colour from yellow to brown and black. They are capable of flying, although they often leap from plant to plant. Thrips move much faster compared to other pests such as mealybugs, which usually hide underleaf and are difficult to spot.
Signs of Infestation
The presence of silvery streaks or spots on leaves, yellowing or brown part of the leaf, often accompanied by black round droppings are signs of thrips outbreak.
Impact on Plants
By feeding on plant juices, thrips can cause significant damage and may transmit plant diseases. Thrips spread fast and can kill a plant within a very short time.
Treatment Strategies
Regular inspection of plants, especially those with yellowing or brown leaves is very important as it can allow you to catch this infestation at a very early stage. Leaves of plants can be cleaned regularly with water or hydrogen peroxide solution to remove single thrips from leaves before those cause any damage and spread. It is always worth trying homemade and natural remedies for thrips. If you want to use pesticides, choose non-toxic and biodegradable options that will not harm pollinators, other animals, and the environment.
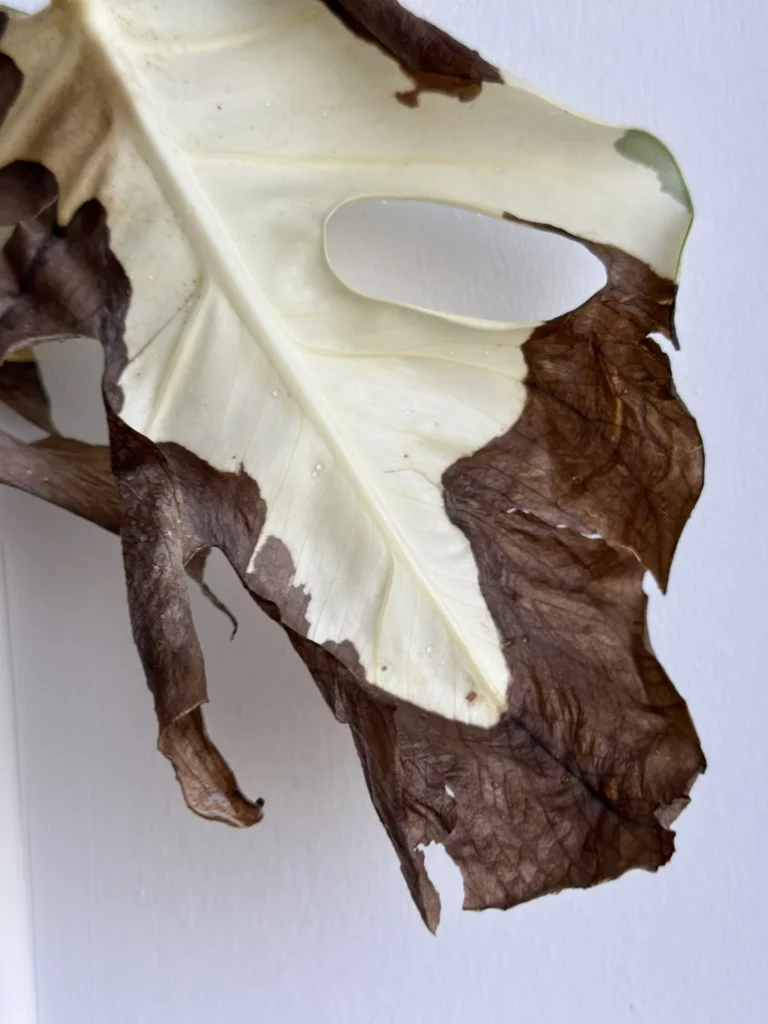
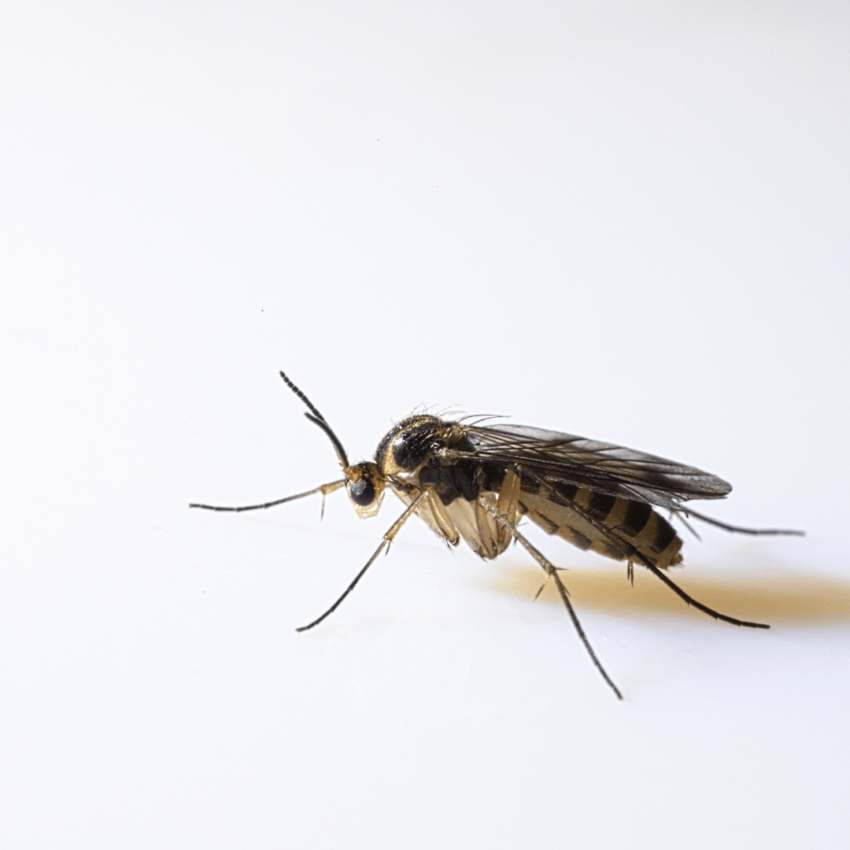
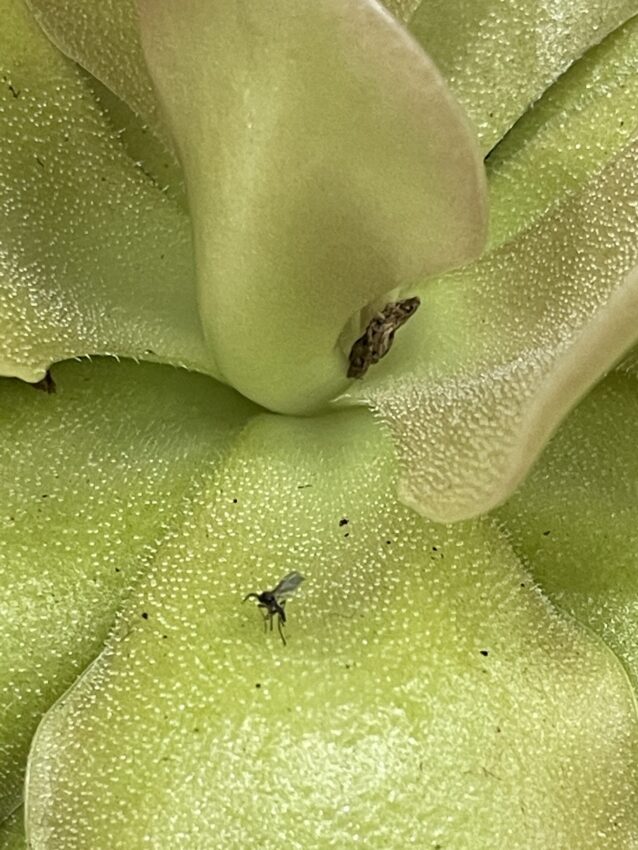
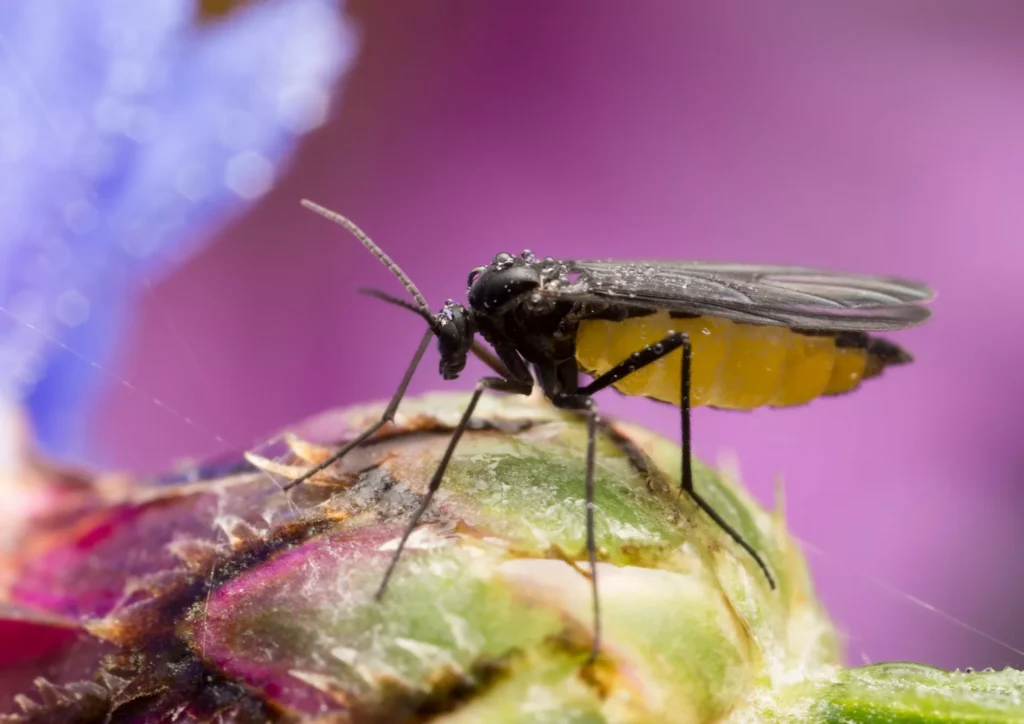
Fungus Gnats: The Tiny Flying Pests
Characteristics
Fungus gnats are small and black, resembling mosquitoes. However, they are not harmful to humans. You can read more about fungus gnats in our article.
Signs of Infestation
You may notice larvae in the soil but more often you will just spot the adult gnats flying around the soil surface. Especially around plants where the soil stays moist for longer.
Impact on Plants
Fungus gnats usually do not cause significant damage to the houseplant and are rather just annoying for people around but in case of a large infestation, larvae may feed on root hairs. This will impact the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients effectively as a result decreasing the growth of the plant and causing plant death,
Treatment Strategies
Bottom watering and keeping the top of the soil dry can help to prevent outbreaks. When repotting plants make sure that the potting mix is from reputable sources. Large garden centres usually store potting mix outside in bags, Fungus gnats lay eggs in the wet soil and as soon as you bring it into a warm and cosy home fungus gnat larva will hatch. One of the best natural prevention and treatment method are carnivorous plants. Using hydrogen peroxide also may help with eliminating fungus gnats if you prefer natural methods.
Conclusion
By understanding the characteristics, signs, and impacts of these common pests on your plants, you’ll be able to spot the issue at the first sign and be better equipped to implement effective treatment and prevention strategies. These strategies will help to ensure that your beautiful indoor jungle will be a thriving, pest-free sanctuary. If you are ever in doubt about a possible pest infestation then get in touch with us via the Plant Hospital on our website and we can diagnose the issue for you.